The mechanism of antidepressant action of a new 3-substituted thiethane-1,1-dioxide derivative in tests of neuropharmacological interaction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3897/rrpharmacology.8.86560Abstract
Introduction: The present study is aimed at investigation of the mechanism of action of a new 3-substituted thietane-1,1-dioxide derivative (N-199/1) exhibiting antidepressant properties, in several tests of neuropharmacological interaction.
Materials and methods: To study the mechanism of action of N-199/1, its effect on 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP)-induced head-twitch response (50 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg), haloperidol-induced catalepsy (1 mg/kg), arecoline-induced tremor (6 mg/kg), picrotoxin-induced seizures (6 mg/kg) and hypothermia, induced by apomorphine (10 mg/kg) or L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA, 140 mg/kg), was assessed when administered singly to white outbred male mice at a dose of 2 mg/kg.
Results and discussion: N-199/1 reduced the number of head twitches, induced by 5-HTP (300 mg/kg), by 83% 45 min after 5-HTP injection; decreased the duration of haloperidol catalepsy by 1–32 s 15–45 min after haloperidol injection; attenuated L-DOPA-induced hypothermia by 0.7 °С and apomorphine-induced hypothermia by 0.6 °С at the timepoint of 30 min; reduced the duration and severity of arecoline tremor and did not affect the convulsive effect of picrotoxin.
Conclusion: N-199/1 acts on serotonergic, noradrenergic, dopaminergic and cholinergic neurotransmission and does not affect neuronal reuptake of monoamines or monoamine oxidase. The mechanism of action of N-199/1 is probably due to stimulation of serotonergic 5HT1A-receptors and/or blockade of 5HT2A/2C-receptors and/or α2-adrenergic receptors; dopaminergic and cholinergic receptors may also be involved.
Graphical abstract: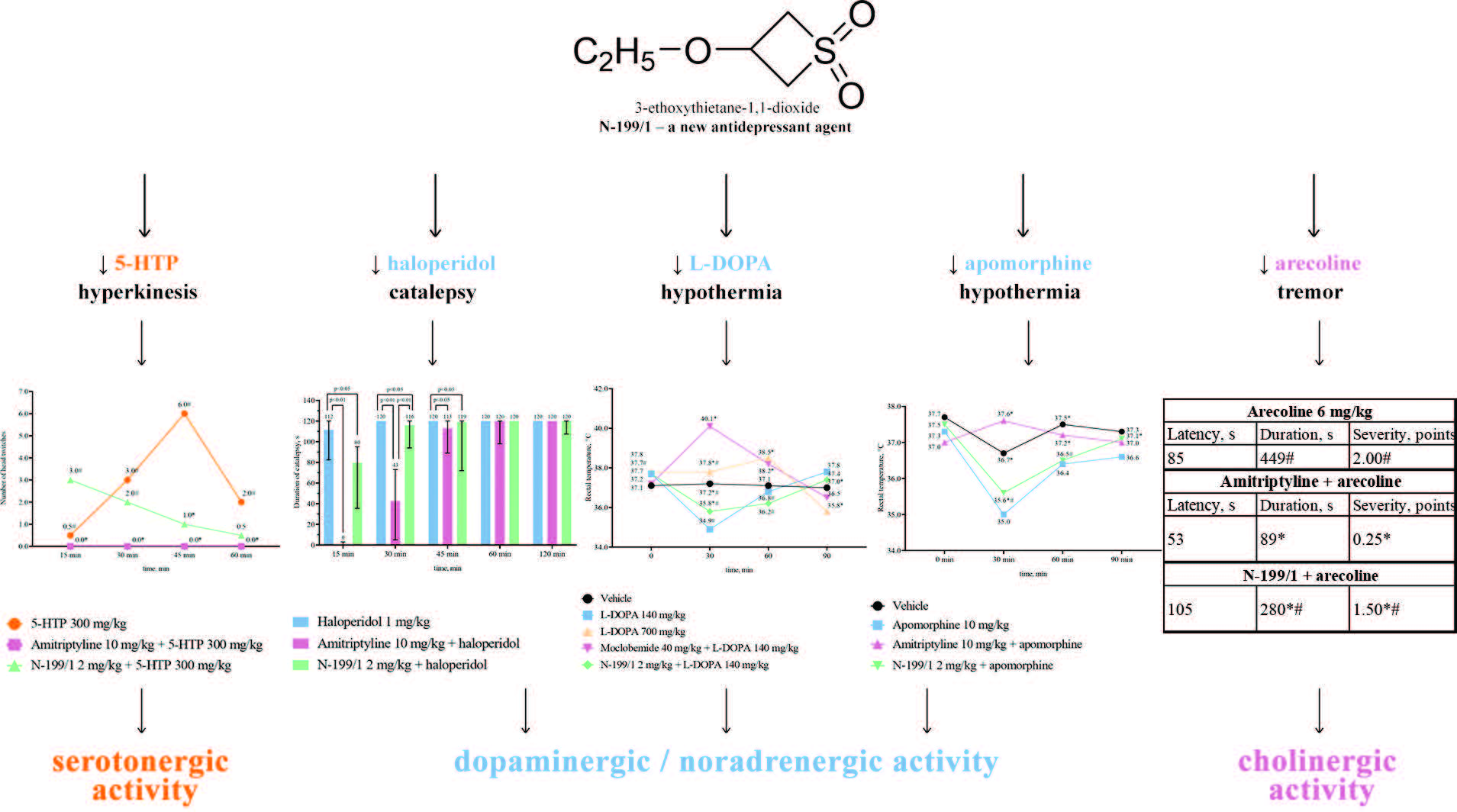
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

