Atherosclerosis is a side effect of cellular senescence
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3897/rrpharmacology.8.81358Abstract
Atherosclerosis is a systemic autoimmune disease of the arterial wall characterized by chronic inflammation, high blood pressure, oxidative stress, and progressive loss of cell and organ function with aging. An imbalance of macrophage polarization is associated with many aging diseases, including atherosclerosis. The polarization toward the pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage is a major promoter of the atheroma formation. It is known that efferocytosis, or ingestion of apoptotic cells, is stimulated by M2 macrophage polarization. A failure of efferocytosis leads to the prolongation of chronic pathology in tissue. In addition, fat-laden macrophages contribute to the plague progression by transforming into foam cells in response to excess lipid deposition in arteries. In spite of the generally accepted theory that macrophages capture oxidized low-density lipoprotein by phagocytosis and become foam cells, we postulate that the main source of lipid accumulation in foam cells are senescent erythrocytes. Senescent erythrocytes lose their plasticity, which affects the rheological blood properties. It is known that their membrane contains high levels of cholesterol. There is evidence that senescent erythrocytes play a pathogenic role in the atheroma formation after breaking down during flowing through an artery bifurcation. Here we review the current knowledge on the impact of age-associated immune cells and red blood cells modifications on atherogenesis.
Graphical abstract: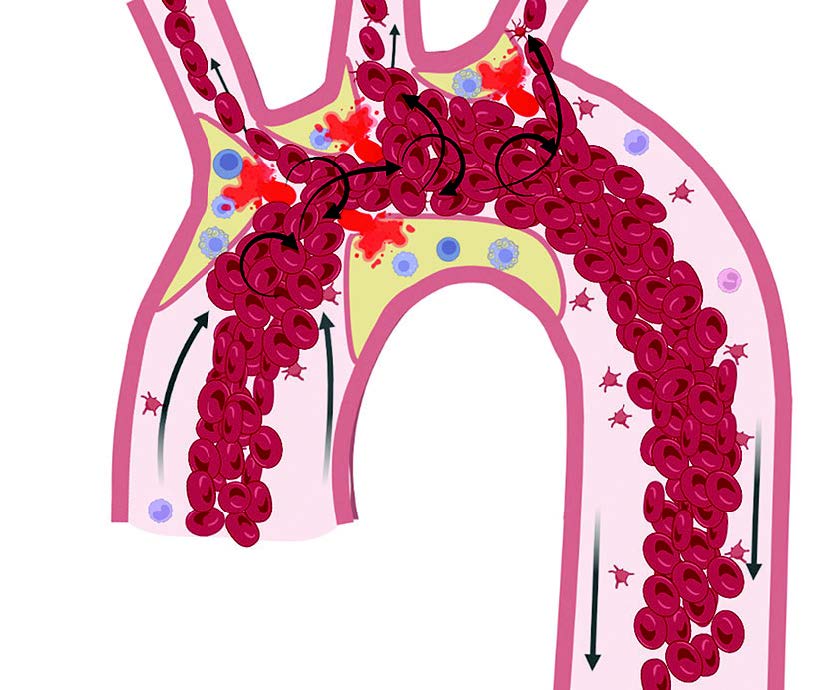
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

