The mitigating effect of a topical preparation of amlodipine on imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like lesion in mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.530Abstract
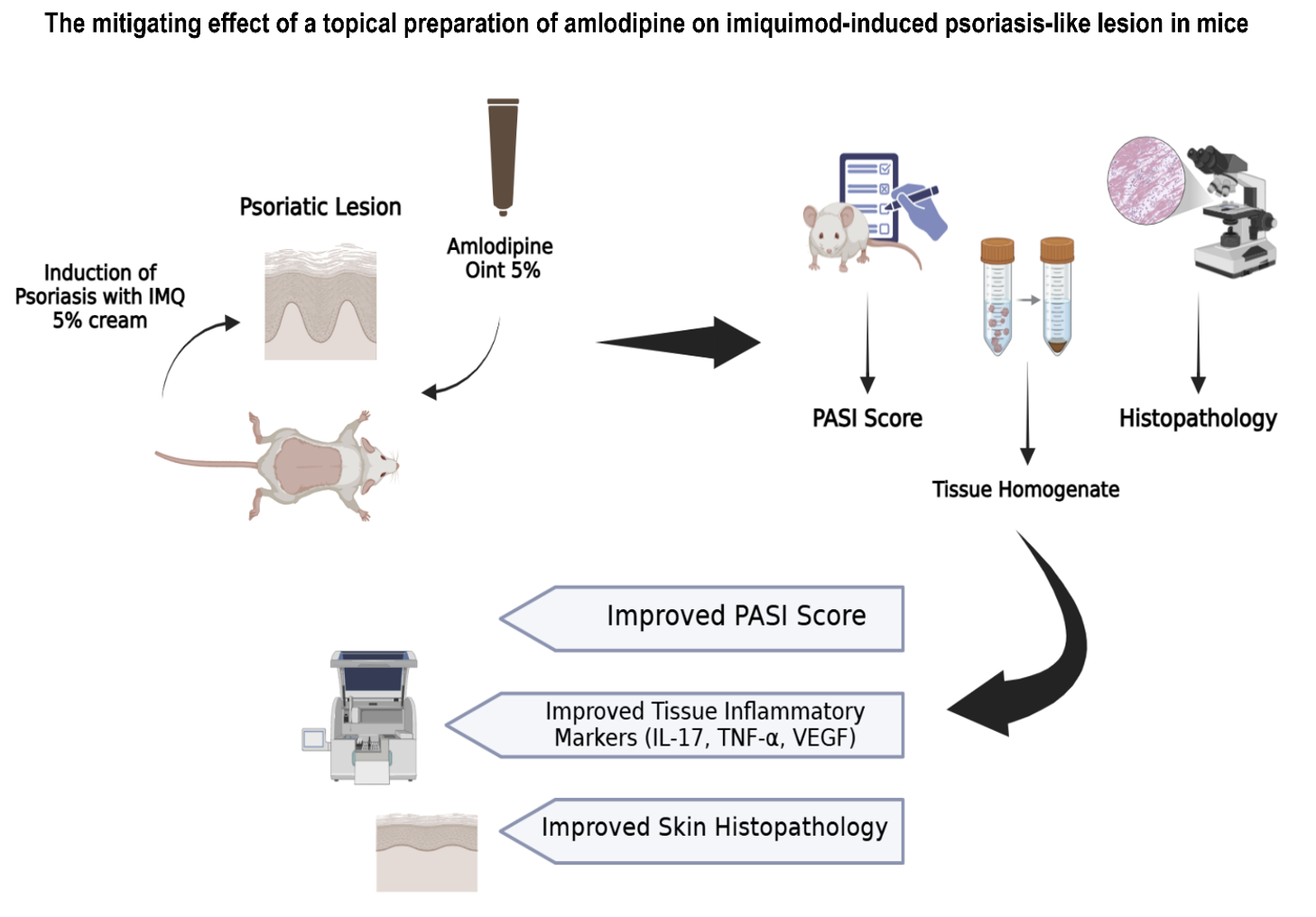
Introduction: Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease depicted by deforming, inconsistent penetrations, and repeated proliferative and inflammatory skin ailment. Local treatment with topical agents is one of the substantial modalities in the remediation of this ailment. Efforts are directed toward the development of novel efficacious topical medicaments. The study examined the potential anti-psoriatic effect of topical amlodipine as a 5% ointment in mice based on observational, histopathological, and biomarker outcomes.
Materials and Methods: Forty-five male Swiss Albino mice were randomly allocated into five distinct groups (I-V), with 9 mice in each group (n=9) that underwent shaving of the dorsal hair. In Group I; animals served as control, while animals of other groups received imiquimod (IMQ) on their shaved backs for six consecutive days to induce psoriasis. Groups from III to V received continuous application of IMQ following day 6 along with a vehicle, clobetasol, andamlodipine 5% ointment for 8 consecutive days. During the timeline of the experiment, observation changes were assessed daily, followed by animal euthanasia and sample collection for biochemical and histopathological evaluation.
Results: Topical amlodipine ointment markedly reduced the inflammatory signs of psoriatic lesions, and histopathological inspection confirmed these findings. The levels of interleukin-17 (IL-17), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-a), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were significantly ameliorated by topical amlodipine Ointment in comparison with the untreated imiquimod-induced psoriatic mice group.
Conclusion: The study concludes that topical amlodipine showed an anti-psoriatic effect comparable to that of topical clobetasol owing to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects making amlodipine a promising agent in the future of psoriasis management as an adjuvant treatment to the standard.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords:
amlodipine, calcium channel blockers, vascular endothelial growth factor, interleukin-17, psoriasis, imiquimodReferences
Abed-Mansoor A and Abu-Raghif AR (2022) Attenuated effects of rivastigmine in induced cytokine storm in mice. Journal of Emergency Medicine, Trauma & Acute Care (3): 12. https://doi.org/10.5339/jemtac.2022.ismc.12
Abu-Raghif AR, Sahib HB, Hanoon MM (2015c) Anti-angiogenic activity of Zizyphus spinachristi Leaves Extracts. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research 35 (1): 169–174.
Almudaris SA, Gatea FK (2024) Effects of topical Ivermectin on imiquimod-induced Psoriasis in mouse model – Novel findings. Pharmacia 71: 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3897/pharmacia.71.e114753
Alsamarai A, Hassan H, Alobaidi A (2019) Association of interleukin-6, interleukin-17 and angiopoietin in different infections, thyroid stimulating hormone, demographic and socioeconomic characteristics in women with bad obstetric history, Kirkuk, Iraq. International Journal of Medical Sciences 2(1): 43–57.
Alwan W and Nestle FO (2015) Pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis: exploiting pathophysiological pathways for precision medicine. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 33(5): S2–S6. [PubMed]
Baek JO, Byamba D, Wu WH, Kim TG and Lee MG (2012) Assessment of an imiquimod-induced psoriatic mouse model in relation to oxidative stress. Archives of Dermatological Research 304(9): 699–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-012-1272-y https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-012-1272-y [PubMed]
Baker BS, Fry L (1992) The immunology of psoriasis. British Journal of Dermatology 126 (1): 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb08394.x
Balak DM, Hajdarbegovic E (2017) Drug-induced psoriasis: clinical perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl) 7: 87–94. https://doi.org/10.2147/ptt.S126727 [PubMed] [PMC]
Bao K, Reinhardt RL (2015) The differential expression of IL-4 and IL-13 and its impact on type-2 immunity. Cytokine 75(1): 25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.008 [PubMed] [PMC]
Calautti E, Avalle L and Poli V (2018) Psoriasis: A STAT3-centric view. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19(1): 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010171 [PubMed] [PMC]
Calkins CM, Bensard DD, Heimbach JK, Meng X, Shames BD, Pulido EJ, McIntyre RC Jr (2001) L-arginine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung chemokine production. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 280(3): L400–L408. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.3.L400 [PubMed]
Carvalho MdFPd, Pereira CSB, Fregnani JH, Ribeiro FdAQ (2015) Comparative histological study on wound healing on rat’s skin treated with Mitomycin C or Clobetasol propionate. Acta Cirúrgica Brasileira 30(9): 593–597. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-865020150090000002 [PubMed]
Charan J and Kantharia ND (2013) How to calculate sample size in animal studies? Journal of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics 4(4): 303–306. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500x.119726 [PubMed] [PMC]
Chen H, Lu C, Liu H, Wang M, Zhao H, Yan Y, Han L (2017) Quercetin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via the NF-κB pathway. International Immunopharmacology 48: 110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.04.022 [PubMed]
Cohen AD, Kagen M, Friger M and Halevy S (2001) Calcium channel blockers intake and psoriasis: a case-control study. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 81(5): 347–349. https://doi.org/10.1080/000155501317140061[PubMed]
Detmar M, Brown LF, Claffey KP, Yeo KT, Kocher O, Jackman RW, Berse B, Dvorak HF (1994) Overexpression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in psoriasis. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 180(3): 1141–1146. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.180.3.1141[PubMed] [PMC]
El Morsy EM, Kamel R and Ahmed MA (2015) Attenuating effects of coenzyme Q10 and amlodipine in ulcerative colitis model in rats. Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology 37(3): 244–251. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2015.1021357 [PubMed]
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods 39(2): 175–191. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03193146 [PubMed]
Fredriksson T, Pettersson U (2009) Severe psoriasis – oral therapy with a new retinoid. Dermatologica 157(4): 238–244. https://doi.org/10.1159/000250839 [PubMed]
Geng X, Shi H, Ye F, Du H, Qian L, Gu L, Wu G, Zhu C, Yang Y, Wang C, Zhou Y, Yu G, Liu Q, Dong X, Yu L, & Tang Z (2018) Matrine inhibits itching by lowering the activity of calcium channel. Scientific Reports 8(1): 11328. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28661-x [PubMed] [PMC]
Ghazy DN, Abu-Raghif AR (2021) Effects of apremilast on induced hypertrophic scar of rabbits. Archives of Razi Institute 76(6): 1803–1813. https://doi.org/10.22092/ARI.2021.356195.1800 [PubMed] [PMC]
Girolomoni G, Strohal R, Puig L, Bachelez H, Barker J, Boehncke WH, Prinz JC (2017) The role of IL-23 and the IL-23/TH 17 immune axis in the pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 31(10): 1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14433 [PubMed] [PMC]
Glitzner E, Korosec A, Brunner PM, Drobits B, Amberg N, Schonthaler HB, Kopp T, Wagner EF, Stingl G, Holcmann M, Sibilia M (2014) Specific roles for dendritic cell subsets during initiation and progression of psoriasis. EMBO Moleculare Medicine 6(10): 1312–1327. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201404114[PubMed] [PMC]
Hasan AM and Gatea FK (2024) Topical apigenin as a promising therapeutic agent for psoriasis: Evaluating efficacy alone and in combination with clobetasol in an imiquimod-induced model of psoriasis in mice. Acta Pharmaceutica Sciencia 62(3): 610–630. https://doi.org/10.23893/1307-2080.APS6239
Huang X, Fan R, Lu Y, Yu C, Xu X, Zhang X, Liu P, Yan S, Chen C, Wang L (2014) Regulatory effect of AMP-activated protein kinase on pulmonary hypertension induced by chronic hypoxia in rats: in vivo and in vitro studies. Molecular Biology Reports 41(6): 4031–4041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3272-9[PubMed]
Hussein Z A, Abu-Raghif A R, Fawzi H A (2024a) The mitigating effect of para-hydroxycinnamic acid in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice through targeting oxidative, inflammatory and fibrotic pathways. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 135(1): 23–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.14018[PubMed]
Hussein ZA, Abu-Raghif AR, Tahseen NJ, Rashed KA, Shaker NS, Fawzi HA (2024b) Vinpocetine alleviated alveolar epithelial cells injury in experimental pulmonary fibrosis by targeting PPAR-γ/NLRP3/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathways. Scientific Reports 14(1): 11131. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61269-y[PubMed] [PMC]
Hussein ZA, Shaker NS, Tahseen NJ, Al-Tuhafi AM, Mutee AF (2020) Possible anti-psoriasis effect of the methanol extract of Phoenix dactylifera L. seeds. Journal of Herbmed Pharmacology 9(4): 382–390. https://doi.org/10.34172/jhp.2020.48
Jeon S, Kim SH, Shin SY, Lee YH (2018) Clozapine reduces Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses through inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent Akt activation in microglia. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 81: 477–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.04.012 [PubMed]
Kang D, Li B, Luo L, Jiang W, Lu Q, Rong M, Lai R (2016) Curcumin shows excellent therapeutic effect on psoriasis in mouse model. Biochimie 123: 73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2016.01.013 [PubMed]
Kaya H, Polat B, Albayrak A, Mercantepe T, Buyuk B (2018) Protective effect of an L-type calcium channel blocker, amlodipine, on paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Human & Experimental Toxicology 37(11): 1169–1179. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327118758382 [PubMed]
Kerdel F, Don F (2018) The importance of early treatment in psoriasis and management of disease progression. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 17: 737–742. [PubMed]
Khorsheed SM, Abu-Raghif AR, Ridha-Salman H (2024) Alleviative effects of combined topical melatonin and rutin on imiquimod-induced psoriasis mouse model. Pharmacia 71: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3897/pharmacia.71.e128832
Kwatra G and Mukhopadhyay S (2018) Topical Corticosteroids: Pharmacology. A Treatise on Topical Corticosteroids in Dermatology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4609_2
Li C, Yao H, Wang H, Fang JY and Xu J (2021) Repurposing screen identifies Amlodipine as an inducer of PD-L1 degradation and antitumor immunity. Oncogene 40: 1128-1146. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01592-6
Li L, Shucheng H, Fu L, Pei B, Xu W, Jiang X (2023) Overexpression and potential roles of midkine via regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A in psoriasis. Experimental Dermatology 32(9): 1383-1393. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.14836
Li Y, Zhang G, Chen M, Tong M, Zhao M, Tang F, Xiao R, Wen H (2019) Rutaecarpine inhibited imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis via inhibiting the NF-κB and TLR7 pathways in mice. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 109: 1876–1883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.062 [PubMed]
Liu X, Yao M, Li N, Wang C, Zheng Y, Cao X (2008) CaMKII promotes TLR-triggered proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon production by directly binding and activating TAK1 and IRF3 in macrophages. Blood 112(13): 4961–4970. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-03-144022 [PubMed]
Lo Y, Lin LY, Tsai TF (2021) Use of calcium channel blockers in dermatology: a narrative review. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 14(4): 481–489. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2021.1894128 [PubMed]
Mahdi ZA, Hussain AM, Alblesh HA (2024) Histopathological and immunological effects of nebivolol 5% topical cream in mice model of imiquimod-induced psoriasis. Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences 6(1): 133–141.
Marina ME, Roman II, Constantin AM, Mihu CM and Tătaru AD (2015) VEGF involvement in psoriasis. Clujul Medical 88(3): 247–252. https://doi.org/10.15386/cjmed-494 [PubMed] [PMC]
Mohammed SS, Kadhim HM, Al-Sudani IM, Musatafa WW (2022) Study the topical effect of six days use of different lycopene doses on imiquimod-induce psoriasis-like skin inflammation in Mice. International Journal of Health Sciences 6(S3): 171–185.
Ni X, Lai Y (2020) Keratinocyte: A trigger or an executor of psoriasis? Journal of Leukocyte Biology 108(2): 485-491. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.5mr0120-439r [PubMed]
Ogretmen Z, Askin U, Hiz MM, Cevizci S (2014) Triggering drug use in patients with psoriasis: an investigative report from Turkey. Advances in Dermatology and Allergology 31(5): 294–298. https://doi.org/10.5114/pdia.2014.44019 [PubMed] [PMC]
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A, Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl U, Emerson M, Garner P, Holgate ST, Howells DW, Karp NA, Lazic SE, Lidster K, MacCallum CJ, Macleod M, Pearl EJ, Petersen OH, Rawle F, Reynolds P, Rooney K, Sena ES, Silberberg SD, Steckler T, Würbel H (2020) The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biology 18(7): e3000411. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411 [PubMed] [PMC]
Ridha-Salman H, Al-Zubaidy AA, Abbas AH, Hassan MD, Malik SA (2024) The alleviative effects of canagliflozin on imiquimod-induced mouse model of psoriasis-like inflammation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03406-y Online ahead of print [PubMed]
Saleh AH, Khalaf JM, Ameen KA (2022) Nano-emulsions as topical delivery for anti-psoriatic drugs (subject review). Eurasian Medical Research Periodical 5: 17–24.
Sankar L, Arumugam D, Boj S, Pradeep P (2017) Expression of angiogenic factors in psoriasis vulgaris. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 11(3): ec23-ec27. 20170301. https://doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2017/23039.9525 [PubMed] [PMC]
Sarac G, Koca TT and Baglan T (2016) A brief summary of clinical types of psoriasis. Northern Clinic of Istanbul 3(1): 79–82. https://doi.org/10.14744/nci.2016.16023 [PubMed] [PMC]
Sheraz MA, Ahsan SF, Khan MF, Ahmed S, Ahmad I (2016) Formulations of amlodipine: A Review. Journal of Pharmaceutics 2016: 8961621. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8961621 [PubMed] [PMC]
Sun J, Xie J, Kang L, Ferro A, Dong L, Xu B (2016) Amlodipine ameliorates ischemia-induced neovascularization in diabetic rats through endothelial progenitor cell mobilization. BioMed Research International 2016: 3182764. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3182764 [PubMed] [PMC]
Underwood W, Anthony R (2020) AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2020 edition. 2020–2021.
van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JS, Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD, Cornelissen F, Mus AM, Florencia E, Prens EP, Lubberts E (2009) Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. The Journal of Immunology 182(9): 5836–5845. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0802999[PubMed]
Yu Y, Blokhuis BR, Garssen J, Redegeld FA (2016) Non-IgE mediated mast cell activation. European Journal of Pharmacology 778: 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.07.017 [PubMed]
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mahdi ZA, Gatea FK, Hassan OM, Hussein ZA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

