Diagnosis and treatment of arterial stiffness, pulmonary hypertension, diastolic cardiac dysfunction against the background of ischaemic heart disease in comorbid patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.518Abstract
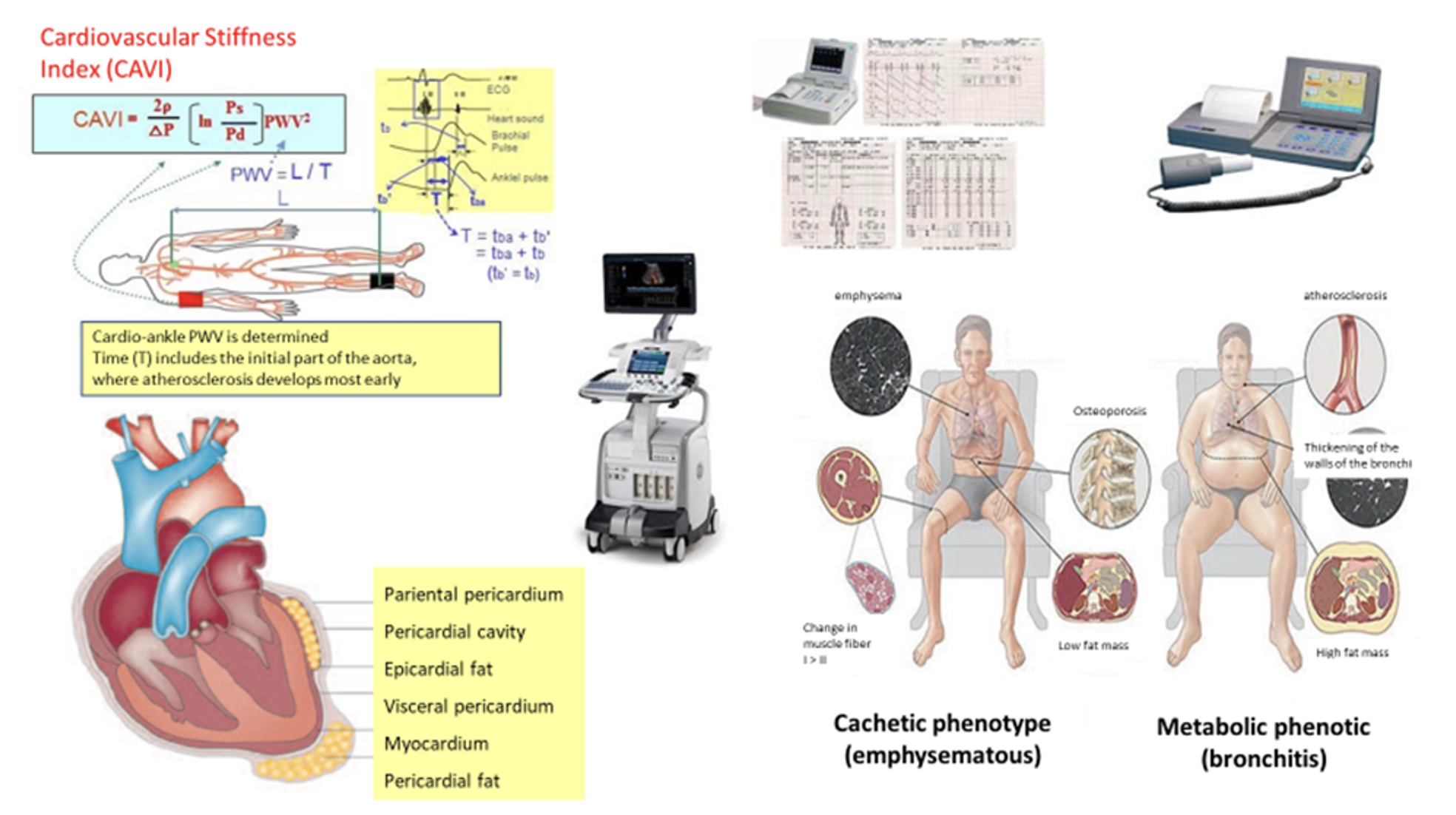
Introduction: In the context of cardiology and neurology, special attention is paid to the problems of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular pathologies, often caused by vascular dysfunction. Haemodynamic parameters, in particular arterial stiffness (AS), and epicardial fat thickness (EFT), play a significant role in the assessment of cardiovascular health. The aim of the study was to evaluate the correlation between arterial stiffness, pulmonary hypertension (PH), epicardial fat thickness and diastolic myocardial dysfunction in comorbid patients.
Materials and Methods: The comparative study was conducted in three groups of patients with the most frequent comorbid pathology. The first group (n=75) included patients with ischaemic heart disease (IHD), arterial hypertension stage II-III and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) stage II-III. The second group (n=50) consisted of patients with IHD and arterial hypertension without COPD. The third group (n=33) included patients with IHD without comorbidities.
Results: The study revealed a significant correlation between indices of AS, blood pressure (BP), EFT and PH in patients with comorbid conditions. The study found that the addition of the combined antihypertensive drug amlodipine-perindopril to standard therapy contributed to normalization of AS, PH and BP during three months of treatment. There was also a significant improvement in the patients’ quality of life, reduction of dyspnoea and heart failure symptoms.
Conclusion: The obtained data confirm the presence of correlation between AS, BP, PH and EFT in patients with IHD, AH and COPD, which may serve as indicators of comorbid diseases. The use of combined antihypertensive drug amlodipine-perindopril seems reasonable and scientifically justified, especially after coronary stenting.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords:
coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, arterial stiffness, pulmonary hypertension, epicardial fat thickness, amlodipine-perindopril, coronary stentingReferences
Belik EV, Gruzdeva OV, Dyleva YA, Borodkina DA, Brel NK, Bychkova EE, Pecherina TB, Karetnikova VN, Kashtalap VV, Palicheva EI, Kuzmina AA, Fanaskova EV, Barbarash OL (2020) Associations of epicardial fat thickness and circulating markers of myocardial fibrosis in patients with myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis [Ateroskleroz] 16(2): 34–42. https://doi.org/10.15372/ATER20200203 [in Russian]
Bontsevich RA, Vovk YR, Gavrilova AA, Kirichenko AA, Krotkova IF, Kosmacheva ED, Kompaniets OG, Prozorova GG, Nevzorova VA, Martynenko IM, Ketova GG, Barysheva VO, Maksimov ML, Osipova OA (2021) Drug therapy of arterial hypertension: assessment of the physicians’ basic knowledge. Final results of the PHYSTARH project. Systemic Hypertension [Sistemnye Gipertenzii] 18(2): 80–87. https://doi.org/10.26442/2075082X.2021.2.200884 [in Russian]
Boytsov SA, Drapkina OM, Shlyakhto EV, Konradi AO, Balanova YA, Zhernakova YV, Metelskaya VA, Oshchepkova EV, Rotar OP, Shalnova SA (2021) ESSE-RF study (Epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases and their risk factors in the regions of the Russian Federation). Ten years later. Cardiovascular Therapy and Prophylaxis [Kardiovaskulyarnaya Terapiya i Profilaktika] 20(5): 3007. https://doi.org/10.15829/1728-8800-2021-3007 [in Russian]
Drapkina OM, Shepel RN, Deeva TA (2018) Epicardial fat thickness – a ‘signature’ of metabolic syndrome. Obesity and Metabolism [Ozhirenie i Metabolizm] 15(2): 29–34. https://doi.org/10.14341/omet9295 [in Russian]
Druzhilov MA, Kuznetsova TY (2019) Visceral obesity as a risk factor for arterial hypertension. Russian Journal of Cardiology [Rossijskij Kardiologicheskij Zhurnal] (4): 7–12. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2019-4-7-12 [in Russian]
Kobalava JD, Konradi AO, Nedogoda SV, Shlyakhto EV, Arutyunov GP, Baranova EI (2020) Arterial hypertension in adults. Clinical Recommendations 2020. Russian Journal of Cardiology [Rossijskij Kardiologicheskij Zhurnal] 25(3): 3786. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2020-3-3786 [in Russian]
Murkamilov IT, Sabirov IS, Fomin VV, Aitbaev KA, Schastlavenko AI, Murkamilova JA, Yusupov FA (2021) Cystatin C, arterial stiffness and echocardiography parameters in patients with respiratory diseases. Pulmonology [Pul'monologiya] 31(4): 407–417. https://doi.org/10.18093/0869-0189-2021-31-4-407-417 [in Russian]
Mustafina IA, Ionin VA, Dolganov AA, Ishmetov VSh, Pushkareva AE, Yagudin TA, Danilko KV, Zagidullin NSh (2022) Role of epicardial adipose tissue in the development of cardiovascular diseases. Russian Cardiological Journal [Rossijskij Kardiologicheskij Zhurnal] 27(1S): 4872. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2022-4872 [in Russian]
Pribylov SA, Leonidova KO, Pribylov VS, Gavrilyuk EV, Pribylova NN (2024) Approaches to therapy Amlodipine/Indapamide/Perindopril therapy of high arterial hypertension in ischemic heart disease patients with chronic kidney disease stage 1-3 after coronary stenting. Research Results in Pharmacology 10(2): 49–55. https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.475 [in Russian]
Pribylova NN, Shabanov EA, Samosudova LV, Novikov MV, Seredin VS, Sidorets VM, Korzun EG (2016) Determination of epicardial fat, endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease associated with ischaemic heart disease and arterial hypertension. Health and Disease Features, p. 299. [in Russian]
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, Barengo NC, Beaton AZ, Benjamin EJ, Benziger CP, Bonny A, Brauer M, Brodmann M, Cahill TJ, Carapetis J, Catapano AL, Chugh SS, Cooper LT, Coresh J, Criqui M, DeCleene N, Eagle KA, Emmons-Bell S, Feigin VL, Fernández-Solà J, Fowkes G, Gakidou E, Grundy SM, He FJ, Howard G, Hu F, Inker L, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Koroshetz W, Lavie C, Lloyd-Jones D, Lu HS, Mirijello A, Temesgen AM, Mokdad A, Moran AE, Muntner P, Narula J, Neal B, Ntsekhe M, Moraes de Oliveira G, Otto C, Owolabi M, Pratt M, Rajagopalan S, Reitsma M, Ribeiro ALP, Rigotti N, Rodgers A, Sable C, Shakil S, Sliwa-Hahnle K, Stark B, Sundström J, Timpel P, Tleyjeh IM, Valgimigli M, Vos T, Whelton PK, Yacoub M, Zuhlke L, Murray C, Fuster V; GBD-NHLBI-JACC (2020) Global Burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 76(25): 2982–3021. https://doi/org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Pribylova NN, Leonidova KO, Pribylov VS, Shabanov EA, Pribylov SA, Novikov NV

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

