Effectiveness of the tetrapeptide HAEE: an innovative approach to Alzheimer's treatment in experimentation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.548Abstract
Introduction: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by a progressive decline in cognitive functions. According to the “Alzheimer’s Disease International”, there were 36 million reported cases of AD worldwide in 2009, with projections suggesting an increase to 66 million by 2030 and 115 million by 2050.
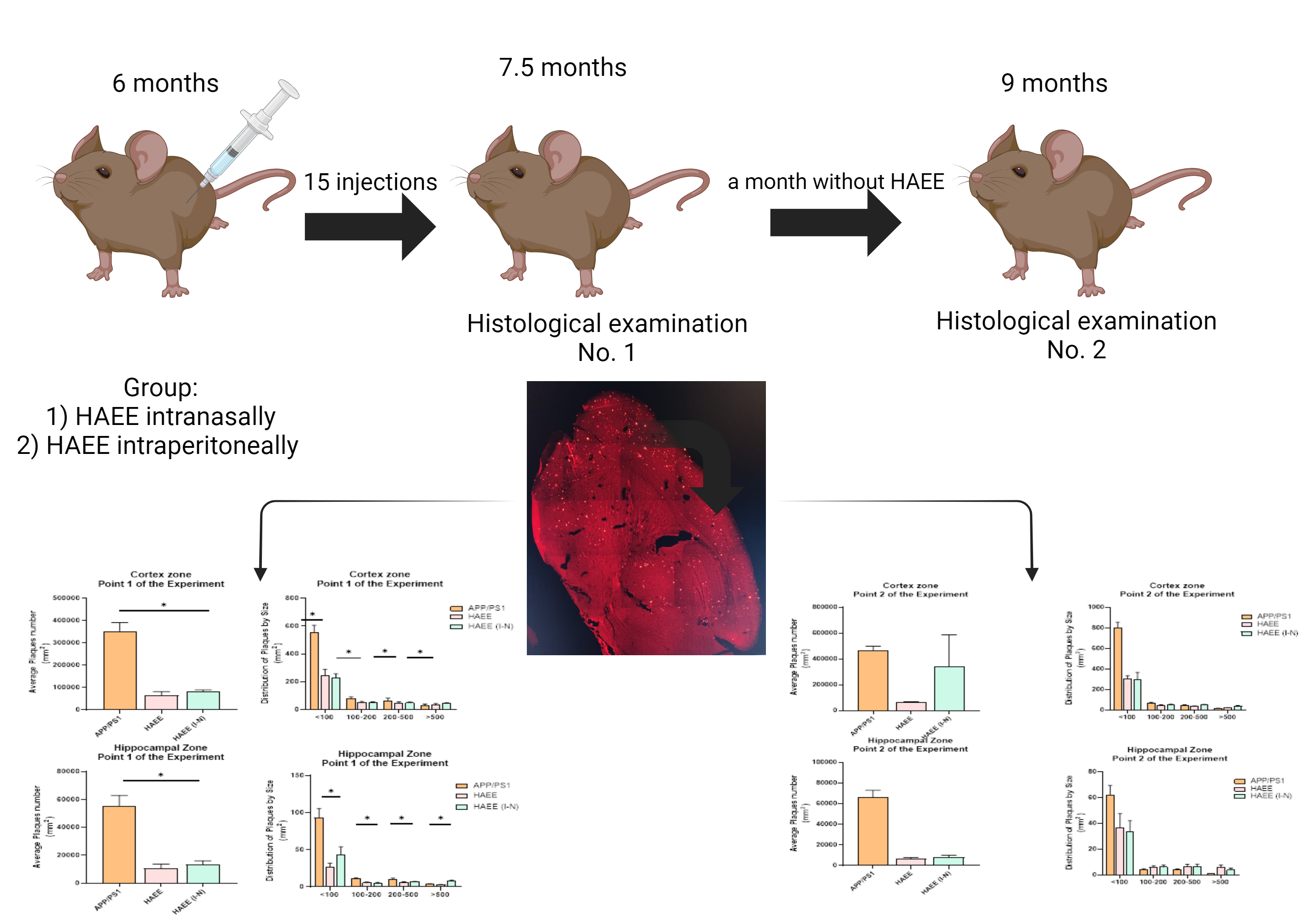
Materials and Methods: The study was conducted on three experimental groups consisting of male APPswe/PS1dE9/Blg mice on a mixed genetic background with C57Bl6/Chg animals. Each group included 10 mice. At the baseline (point 0), peptides and drugs were administered to two groups of animals aged 6 months. The treatments were given circadianly every 48 hours without breaks for one month. Subsequently, at point 1 of the experiment, half of the group (n=5) was selected for further histological analysis of the brain. The remaining half did not receive any treatments for one month before undergoing histological examination. Statistical significance between experimental and control groups was assessed using an unpaired Student’s t-test at p<0.05.
Results and Discussion: Histological analysis indicated the efficacy of the tetrapeptide HAEE at a dosage of 50 mg per kg of mouse weight, showing a significant reduction in amyloid plaques in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of the mice.
Conclusion: The study supports the proposed hypotheses and suggests further investigation into additional drug groups recommended for Alzheimer’s treatment for comparative studies.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords:
tetrapeptide, Alzheimer's disease, HAEE, treatment, APP/PSEN1References
Bach J, Haeusler D, Schmitt F (2020) The challenges of amyloid-targeting therapies in Alzheimer's disease: A critical appraisal. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 78(3): 921–935. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-200118
Froelich L, Haeusler D, Hoyer S (2019) Limitations of peptide-based treatments for Alzheimer's disease: An overview of the current status and future directions. Neuropharmacology 148: 146–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.004
Korokin MV, Gudyrev OS, Pokrovskaya TG, Danilenko LM, Zhernakova NI, Avtina TV, Parshina AV, Pribylov SA, Lebedev PR, Kochkarov AA, Kuzubova EV, Radchenko AI, Koklin IS, Taran EI (2023) Features of bone remodeling and osteoreparation processes in modeling femoral fracture in genetically modified mice with impaired enzymatic regulation of steroid hormone metabolism. Research Results in Pharmacology 9(4): 113–123. https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.9.10062
Lysikova EA, Kuzubova EV, Radchenko AI, Patrakhanov EA, Chaprov KD, Korokin MV, Deykin AV, Gudyrev OS, Pokrovskii MV (2023) The APPswe/PS1dE9/Blg transgenic mouse line for modeling cerebral amyloid angiopathy associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular Biology 57(1): 74–82. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893323010077[PubMed]
Polikarpova AV, Egorova TV, Bardina MV (2022) Genetically modified animal models of hereditary diseases for testing of gene-directed therapy. Research Results in Pharmacology 8(2): 11–26. https://doi.org/10.3897/rrpharmacology.8.82618
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li Z, Zhang L (2021) Limitations of current therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 13: 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.754123
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Patrakhanov EA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

