New compounds with a dihydropyridine framework as promising hypolipidemic and hepatoprotective agents
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.483Abstract
Introduction: To solve the problem of complex and safe pharmacological correction of metabolic disorders, including hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, and liver lesions is currently very important. With this in mind, the new derivatives of cyanothioacetamide with a dihydropyridine framework, with a potential effect on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism and the functioning of the liver are of great interest.
Materials and Methods: To conduct an experiment, three samples were selected from an extensive library of new cyanothioacetamide derivatives, which, according to in silico studies, proved promising towards the positive effect on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, as well as towards the protective effect on the liver. To study the compounds in vivo, metabolic disorders were simulated in Wistar rats by long -term alimentary and subsequent dexamethasone loads. The pharmacological efficacy of new compounds AZ-383, AZ-257, AZ-020 (administered in a dose of 1 mg/kg for 14 days) was assessed in comparison with metformin (300 mg/kg for 14 days) and vildagliptin (8 mg/kg for 14 days) by determining the biochemical indicators of blood (ALT, AST, total bilirubin, total cholesterol, triglycerides, and glucose), morphological and morphometric studies of the liver sections, and the study of immunohistochemical indicators of hepatocyte proliferation. The experimental results were statistically processed using the recognized methods of mathematical statistics. When processing the experimental data, the average arithmetic (AA) was determined. The statistical significance of the compared options was determined on the basis of the Student’s t-test, with the critical value of the Student’s t-test equal to 2.101 and the significance level α = 0.05.
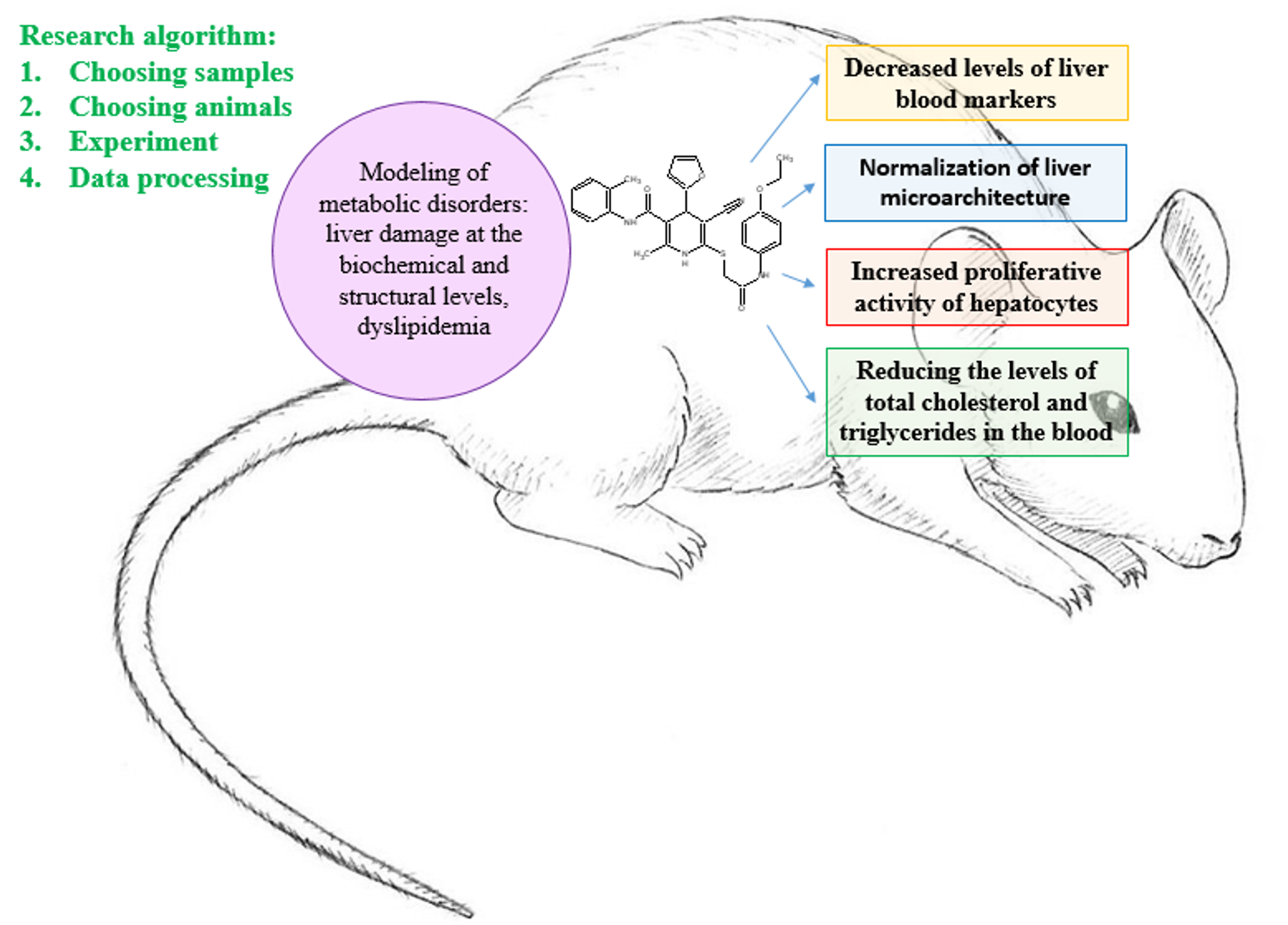
Results: The study shows that all the new compounds studied in the experiment – AZ-383, AZ-257, AZ-020 – have hypolipidemic and hepatoprotective properties, which manifested in the reduced levels of liver biochemical markers of blood, which had increased after simulating metabolic disorders, in the reduced concentration of total cholesterol and triglycerides in blood, in the normalization of liver microarchitecture, as well as in the proliferative activity of hepatocytes.
Discussion: The hepatoprotective and hypolypidemic properties of the new derivatives of cyanothioacetamide with a dihydropyridine framework, which were determined while conducting the experiment, can be accounted for by their effects on the biotargets, identified for AZ-383, AZ-257, and AZ-020 in silico. According to the results, the most pronounced hepatoprotective activity was found in AZ-383 (intragastrically, 1 mg/kg for 14 days). The Ki-67 proliferation index under the influence of this compound was registered at the level of 1.48±0.03%, which exceeds this indicator in the control animals and proves a significant hepatoprotective activity of AZ-383.
Conclusion: The results show good prospects and high efficacy of the new studied cyanothioacetamide derivatives, such as AZ-383, AZ-257, AZ-020 (in a dose of 1 mg/kg), in terms of comprehensive correction of metabolic disorders. Further study is needed for this class of compounds.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords:
new cyanothioacetamide derivatives with a dihydropyridine framework, metabolic disorders,, hyperlipidemia, hepatoprotective activity, pharmacological correctionReferences
Ametov AS, Kamynina LL, Litvinenko VM (2018) Hypoadiponectinemia is a marker of glucose and lipotoxicity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and visceral obesity. Endocrinology: News. Opinions. Education 2 (23): 35–45. https://doi.org/10.24411/2304-9529-2018-12003 [PubMed] [PMC]
Amlaev KR (2021) Dyslipidemia: Epidemiology, clinical picture, diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Doctor [Vrach] 5: 16–20. https://doi.org/10.29296/25877305-2021-05-03 [in Russian]
Amlaev KR, Dakhkilgova KhT (2020) Obesity: Epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, comorbidity, diagnosis and treatment. Medical Bulletin of the North Caucasus 15 (3): 434–439. https://doi.org/10.14300/mnnc.2020.15104
Balukova EV, Uspensky YuP, Fominykh YuA (2018) Liver lesions of various origins (toxic, drug-induced, dysmetabolic): from etiological heterogeneity to a single unified therapy for patients. RMJ. Medical Review [Russkij Medicinskij ZHurnal] 26 (1): 35–40. [in Russian]
Bibik EY, Saphonova AA, Yeryomin AV, Frolov KA, Dotsenko VV, Krivokolysko SG (2017) Search for agents with anti-inflammatory activity among tetrahydropyrido[2,1-b][1,3,5]thiadiazine derivatives. Chemical-Pharmaceutical Journal 51(8): 16–19. https://doi.org/10.30906/0023-1134-2017-51-8-16-19
Bibik EYu, Saphonova AA, Yeryomin AV et al. (2017) Study of analeptic activity of tetrahydropyrido [2,1-b] [1,3,5] tiadiazine derivatives. Research Result in Pharmacology 3(4): 20–25. https://doi.org/10.18413/2313-8971-2017-3-4-20-25
Chaulin AM (2019) Adenosine and its role in the physiology and pathology of the cardiovascular system. Cardiology: News. Opinions. Education 3(22): 37–45. https://doi.org/10.24411/2309-1908-2019-13004
Chaulin AM (2020) New groups of lipid-lowering drugs based on inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 (PCSK9). Part 1. Clinical Medicine [Klinicheskaya Medicina] 98 (11-12): 739–744. https://doi.org/10.30629/0023-2149-2020-98-11-12-739-744
Chazova IE, Shestakova MV, Zhernakova YuV (2021) Eurasian recommendations for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases in patients with diabetes and prediabetes. Eurasian Cardiology Journal [Evrazijskij Kardiologicheskij ZHurnal] 2: 6–61. https://doi.org/10.38109/2225-1685-2021-2-6-61
Chulanova AA, Smakhtina AM, Mal GS, Bobyntsev II, Mishina ES, Smakhtin MY, Kopeykin PM, Bogomolova EG (2024) Protective effects of thymogen analogues, modified by D-alanine, in hydrazine liver damage.Research Results in Pharmacology 10(2): 11–16. https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.458
Dedov II, Shestakova MV, Melnichenko GA (2021) Interdisciplinary clinical recommendations “Treatment of obesity and comorbid diseases”. Obesity and Metabolism [Ozhirenie i Metablizm] 1: 5–99. https://doi.org/0.14341/omet12714 [in Russian]
Druk IV, Ryapolova ЕА (2016) Metformin: Updated recommendations and pleiotropic potential. Therapy [Terapiya] 4(8): 44–51. [in Russian]
Druzhilov MA, Kuznetsova TYu, Chumakova GA (2021) Promising directions for pharmacotherapy of obesity. Russian Journal of Cardiology [Rossijskij Kardiologicheskij ZHurnal] 26(3): 4279. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2021-4279 [in Russian]
Dyachenko VD, Dyachenko IV, Nenaidenko VG (2018) Cyanothioacetamide is a multifunctional reagent with great synthetic capabilities. Advances in Chemistry 87(1): 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4760
Kim OT, Drapkina OM (2022) The obesity epidemic through the prism of evolutionary processes. Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention [Kardiovaskulyarnaya Terapiya i Profilaktika] 21(1): 72–79. https://doi.org/10.15829/1728-8800-2022-3109 [in Russian]
Kozlovskaya SP, Konevalova NYu, Kozlovsky VI, Olenskaya TL (2006) Ezetimibe in the correction of hyperlipidemia. Bulletin of Vitebsk State Medical University [Vestnik Vitebskogo Gosudarstvennogo Medicinskogo Universiteta] 5(2): 11–16. [in Russian]
Lim S, Bae JH, Kwon HS, Nauck MA (2021) COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 17 (1): 11–30. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4 [PubMed] [PMC]
Litvinov VP (2003) Multicomponent cascade heterocyclization - a promising route for the targeted synthesis of polyfunctional pyridines. Advances in Chemistry [Uspekhi Himii] 72(1): 75–92. [in Russian]
Litvinova ES, Konoplya NN, Shulginova AA, Kharchenko AV (2021) Proteins of allogeneic hepatocytes and pharmacological preparations for the correction of immunometabolic disorders in experimental liver pathology.Research Results in Pharmacology 7(2): 83–99. https://doi.org/10.3897/rrpharmacology.7.70314
Liu D, Ahmet A, Ward L, Krishnamoorthy P, Mandelcorn ED, Leigh R, Brown JP, Cohen A, Kim H (2013) A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology 9: 30. https://doi.org/10.1186/1710-1492-9-30 [PubMed] [PMC]
Medvedeva EA, Grigorenko ЕА, Mitkovskaya NP (2023) Innovative lipid-lowering therapy: experience of using inclisiran in the Republic of Belarus. Russian Journal of Cardiology [Rossijskij Kardiologicheskij ZHurnal] 28(4): 5417. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2023-5417 [in Russian]
Meldekhanov TT, Kuttybaev AD, Imanbekova ZhA, Terlikbaeva GA (2019) Toxic drug-induced liver damage. Bulletin of the Kazakh National Medical University [Vestnik Kazahskogo Nacional'nogo Medicinskogo Universiteta] 1: 63–66. [in Russian]
Mullan MJ, Paris D, Pancham B (2007) Compounds and combinations thereof for inhibiting beta-amyloid production and methods of use thereof. Patent application р 347 p.
Muzyko EA, Perfilova VN (2022) The role of adenosine receptors of the A2A subtype in inflammation. Volgograd Scientific and Medical Journal 19(2): 5–11. [in Russian]
Osolodkin DI, Kozlovskaya LI, Dueva EV, Dotsenko VV, Rogova YV, Frolov KA, Krivokolysko SG, Romanova EG, Morozov AS, Karganova GG, Palyulin VA, Pentkovski VM, Zefirov NS (2013) Inhibitors of tick-borne flavivirus reproduction from structure-based virtual screening. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 4 (9): 869–874. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml400226s [PubMed] [PMC]
Polyakova OA, Cheremushkin SV, Ostroumova OD (2023) Correction of hypertriglyceridemia as one of the basis for reducing residual cardiovascular risk: focus on fenofibrate. Cardiology: News, Opinions, Training [Kardiologiya: Novosti, Mneniya, Obuchenie] 11 (1): 42–50. https://doi.org/10.33029/2309-1908-2023-11-1-42-50 [in Russian]
Ray KK, Reeskamp LF, Laufs U, Banach M, Mach F, Tokgözoğlu LS, Connolly DL, Gerrits AJ, Stroes ESG, Masana L, Kastelein JJP (2022) Combination lipid-lowering therapy as first-line strategy in very high-risk patients. European Heart Journal 43(8): 830–833. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab718 [PubMed]
Rice WG, Turpin JA (1996) Virus-encoded zinc fingers as targets for antiviral chemotherapy. Reviews in Medical Virology 39(19): 3606–3616. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1654(199612)6:4<187::AID-RMV176>3.0.CO;2-F [PubMed]
Tereshchuk LV, Mamontov AS, Starovoyova KV (2014) Palm oil fractionation products in the production of spreads. Equipment and Technology of Food Production [Tekhnika i Tekhnologiya Pishchevyh Proizvodstv] 3: 79–83. [in Russian]
Vatutin NT, Taradin GG, Rakitskaya IV et al. (2020) Lipid-lowering therapy in special situations. Health, Food & Biotechnology 2(4): 12–27. https://doi.org/10.36107/hfb.2020.i4.s88 [in Russian]
Wang AL, Iadecola С, Wang G (2017) New generations of dihydropyridines for treatment of hypertension. Journal of Geriatric Cardiology 14 (1): 67. https://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2017.01.006 [PubMed] [PMC]
Zvenigorodskaya LA, Petrakov AV, Nilova TV, Varvanina GG, Lychkova AE (2016) The role of bile acids in the regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes. Experimental and Clinical Gastroenterology [Eksperimental'naya I Klinicheskaya Gastroenterologiya] 11(135): 31–34. [in Russian]
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Elena S. Ketova, Anna V. Myazina, Elena Yu. Bibik, Sergey G. Krivokolysko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

