Влияние каппа-опиоидного агониста U-50488 и ингибитора p38 MAPK на спайковую активность пирамидных нейронов базолатерального миндалевидного тела
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.400Аннотация
Введение: Активация каппа-опиоидных рецепторов (КОР) в базолатеральном миндалевидном теле лежит в основе каппа-опосредованных аверсивных реакций. Цель настоящего исследования заключалась в изучении моно- и комбинированных эффектов соединений U-50488 и SB203580 на спайковую активность пирамидных нейронов в базолатеральном миндалевидном теле, чтобы выявить сложные взаимосвязи между КОР, p38 MAPK и возбудимостью нейронов.
Материалы и методы: Электрофизиологические эксперименты проводились с использованием метода локальной фиксации потенциала в конфигурации “whole-cell”. Подготавливались срезы головного мозга крысы в проекции базолатерального миндалевидного тела, под визуальным контролем устанавливали контакт с пирамидными нейронами базолатеральной миндалины, регистрацию потенциала проводили в режиме фиксации трансмембранного тока (“current clamp mode”). Нейроны идентифицировали по их свойствам аккомодации, сигналы нейронной активности усиливали и анализировали. После локальной перфузии исследуемых соединений были получены 3 кривые доза-эффект для: a) U-50488 (0.001–10 μM); b) комбинации U-50488 (0.001–10 μM) и SB203580 (1 μM); c) комбинации U-50488 (0.01–10 μM) и SB203580 (5 μM).
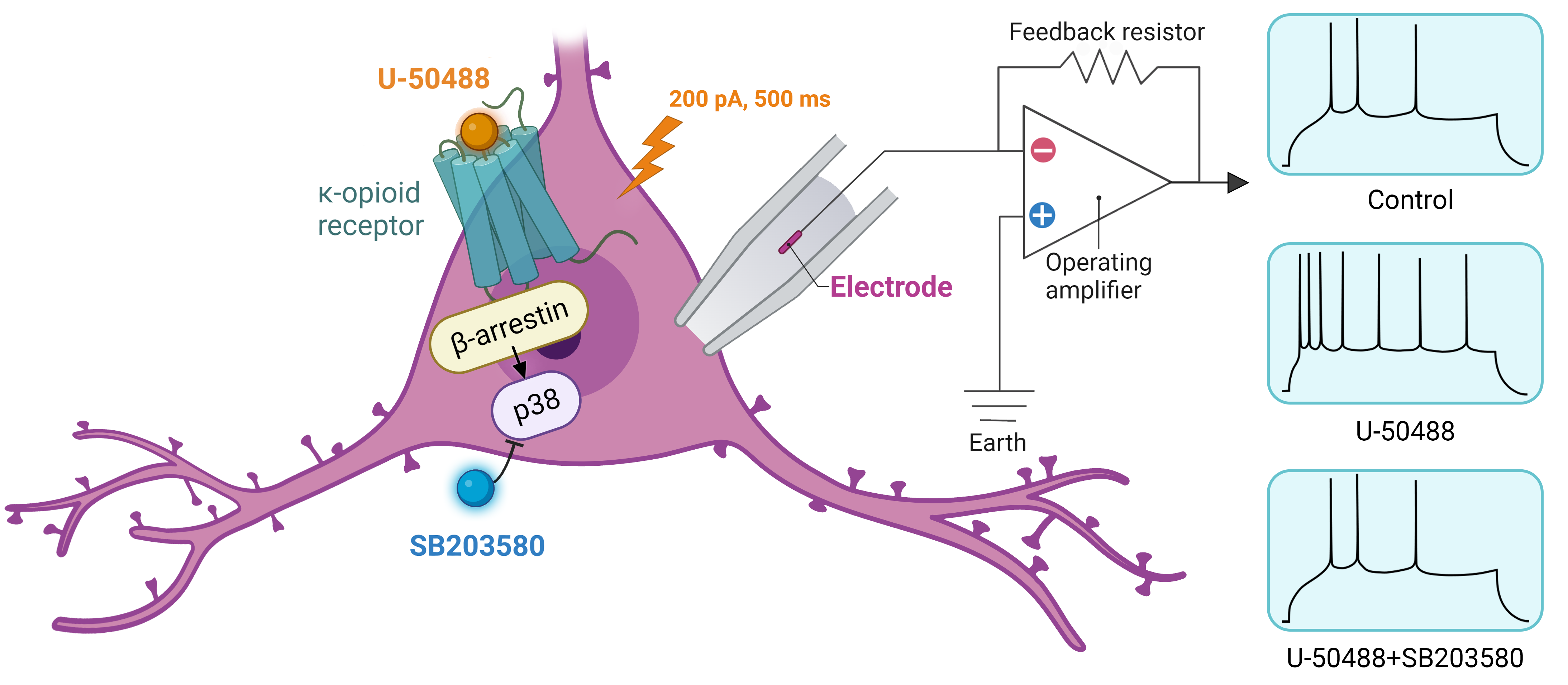
Результаты: После аппликации соединения U-50488 наблюдалось увеличение частоты генерации потенциалов действия пирамидными нейронами в ответ на инъекцию тока, в сравнении с показателями контрольных нейронов (p<0.001). Полученные дозозависимые кривые указывают на неконкурентный антагонизм для комбинации соединений U-50488 и SB203580. Этот вывод подтверждается изменением наклона кривой с уменьшением максимального эффекта U-50488. Таким образом, можно предположить, что увеличение спайковой активности пирамидных нейронов миндалины опосредованно через путь бета-аррестина. При блокировании данного пути, величина спайковой активности возвращается к исходному уровню.
Заключение: В нашем исследовании показано, что индуцированная каппа-опиоидным агонистом спайковая активность пирамидных нейронов опосредована через бета-аррестин и может быть подавлена введением ингибитора p38 MAPK SB203580.
Графическая аннотация
Ключевые слова:
Каппа-опиоидный рецептор, p38 MAPK, миндалевидное тело, пирамидные нейроны, patch clamp, электрофизиология, аверсияБиблиографические ссылки
Bruchas MR, Land BB, Lemos JC, Chavkin C (2009) CRF1-R activation of the dynorphin/kappa opioid system in the mouse basolateral amygdala mediates anxiety-like behavior. PloS One 4(12): e8528. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008528 [PubMed] [PMC]
Dampney RAL (2019) Chapter 28 – Central Mechanisms Generating Cardiovascular and Respiratory Responses to Emotional Stress. In: Fink G (Eds) Stress: Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pathology, Academic Press, pp. 396–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813146-6.00028-X
Franco-García A, Fernández-Gómez FJ, Gómez-Murcia V, Hidalgo JM, Milanés MV, Núñez C (2022) Molecular mechanisms underlying the retrieval and extinction of morphine withdrawal-associated memories in the basolateral amygdala and dentate gyrus. Biomedicines 10(3): 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030588 [PubMed] [PMC]
Franco-García A, Gómez-Murcia V, Fernández-Gómez FJ, González-Andreu R, Hidalgo JM, Victoria Milanés M, Núñez C (2023) Morphine-withdrawal aversive memories and their extinction modulate H4K5 acetylation and Brd4 activation in the rat hippocampus and basolateral amygdala. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 165: 115055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115055 [PubMed]
Janak PH, Tye KM (2015) From circuits to behaviour in the amygdala. Nature 517(7534): 284–292. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14188 [PubMed] [PMC]
Ji G, Sun H, Fu Y, Li Z, Pais-Vieira M, Galhardo V, Neugebauer V (2010) Cognitive impairment in pain through amygdala-driven prefrontal cortical deactivation. The Journal of Neuroscience 30(15): 5451–5464. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0225-10.2010 [PubMed] [PMC]
Khan MI H, Sawyer BJ, Akins NS, Le HV (2022) A systematic review on the kappa opioid receptor and its ligands: New directions for the treatment of pain, anxiety, depression, and drug abuse. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 243: 114785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114785 [PubMed]
Knoll AT, Muschamp JW, Sillivan SE, Ferguson D, Dietz DM, Meloni EG, Carroll FI, Nestler EJ, Konradi C, Carlezon WA Jr (2011) Kappa opioid receptor signaling in the basolateral amygdala regulates conditioned fear and anxiety in rats. Biological Psychiatry 70(5): 425–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.03.017 [PubMed] [PMC]
Lamotte G, Shouman K, Benarroch EE (2021) Stress and central autonomic network. Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic & Clinical 235: 102870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2021.102870 [PubMed]
Michely J, Rigoli F, Rutledge RB, Hauser TU, Dolan RJ (2020) Distinct Processing of Aversive Experience in Amygdala Subregions. Biological psychiatry. Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging 5(3): 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2019.07.008 [PubMed] [PMC]
Navratilova E, Ji G, Phelps C, Qu C, Hein M, Yakhnitsa V, Neugebauer V, Porreca F (2019) Kappa opioid signaling in the central nucleus of the amygdala promotes disinhibition and aversiveness of chronic neuropathic pain. Pain 160(4): 824–832. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001458 [PubMed] [PMC]
Przybysz KR, Werner DF, Diaz MR (2017) Age-dependent regulation of GABA transmission by kappa opioid receptors in the basolateral amygdala of Sprague-Dawley rats. Neuropharmacology 117: 124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.036[PubMed] [PMC]
Sah P, Faber ES, Lopez De Armentia M, Power J (2003) The amygdaloid complex: anatomy and physiology. Physiological Reviews 83(3): 803–834. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00002.2003 [PubMed]
Varlinskaya EI, Johnson JM, Przybysz KR, Deak T, Diaz MR (2020) Adolescent forced swim stress increases social anxiety-like behaviors and alters kappa opioid receptor function in the basolateral amygdala of male rats. Progress in Neuro-psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 98: 109812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109812 [PubMed] [PMC]
Wang DV, Wang F, Liu J, Zhang L, Wang Z, Lin L (2011) Neurons in the amygdala with response-selectivity for anxiety in two ethologically based tests. PloS One 6(4): e18739. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018739 [PubMed] [PMC]
Yakhnitsa V, Ji G, Hein M, Presto P, Griffin Z, Ponomareva O, Navratilova E, Porreca F, Neugebauer V (2022) Kappa opioid receptor blockade in the amygdala mitigates pain like-behaviors by inhibiting corticotropin releasing factor neurons in a rat model of functional pain. Frontiers in Pharmacology 13: 903978. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.903978[PubMed] [PMC]
Zan GY, Wang Q, Wang YJ, Chen JC, WuX, Yang CH, Chai JR, Li M, Liu Y, Hu XW, Shu XH, Liu JG (2016) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in amygdala mediates κ opioid receptor agonist U50,488H-induced conditioned place aversion. Neuroscience 320: 122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.01.052 [PubMed]
Загрузки
Опубликован
Как цитировать
Выпуск
Раздел
Лицензия
Copyright (c) 2024 Konstantin Y. Kalitin, Alexander A. Spasov, Olga Y. Mukha

Это произведение доступно по лицензии Creative Commons «Attribution» («Атрибуция») 4.0 Всемирная.
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

