Влияние экзогенного рекомбинантного HSP 70 на изменение жесткости мембраны нейронов гиппокампа после моделирования неонатальной гипоксии ишемии плода у мышей
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.10.547Аннотация
Введение: Использование атомно-силовой микроскопии для исследования жесткости мембраны нейронов предоставляет ценную информацию о клеточных механизмах и их изменениях в ответ на различные патофизиологические состояния. Белок теплового шока HSP 70, компонент системы ответа на клеточный стресс выполняет функцию стабилизации белковых структур клеточных органелл, однако исследования изменений жесткости клеточной мембраны нейронов гиппокаипа в его присутствии обусловленного нарушением церебрального кровообращения не проводилось.
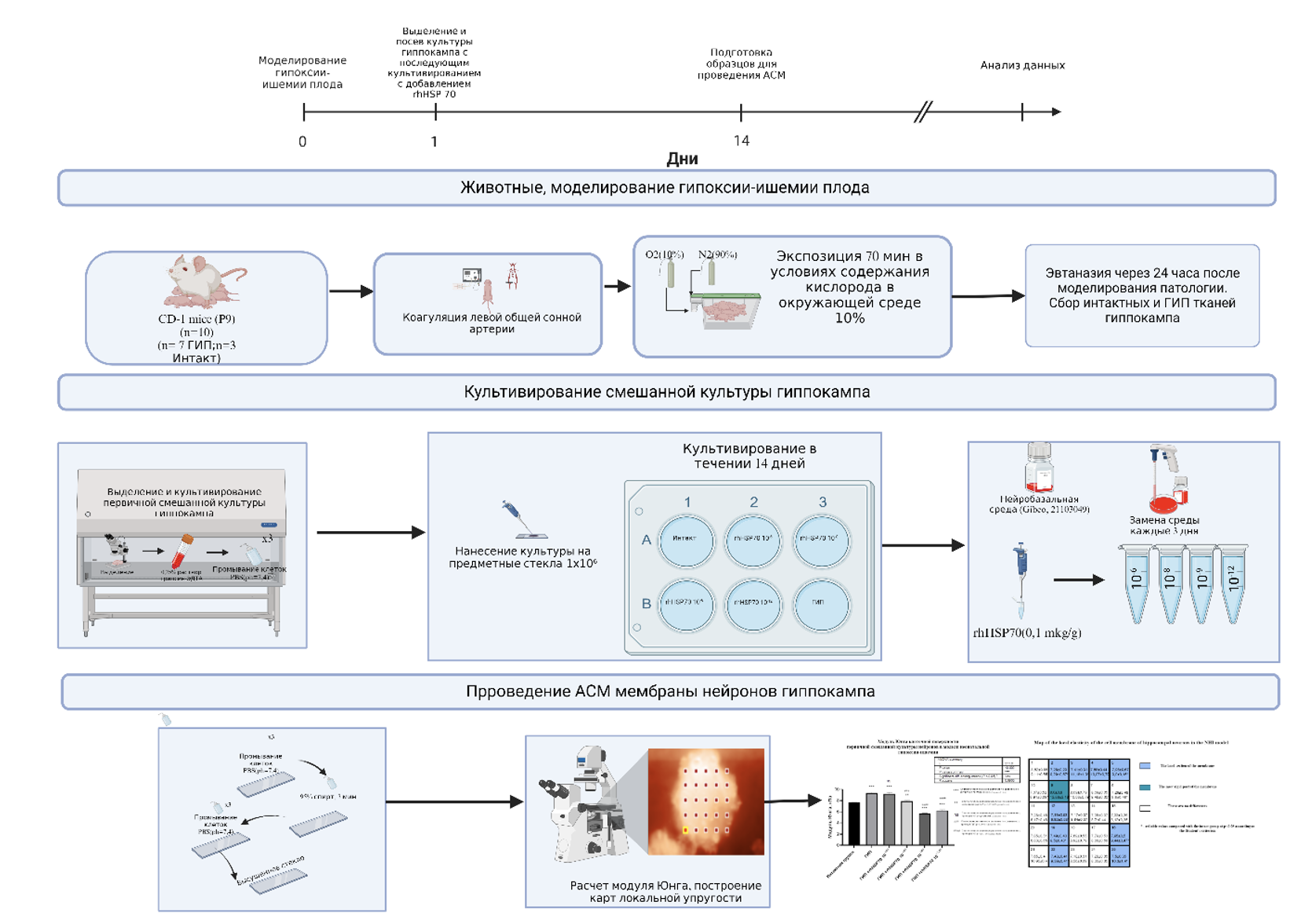
Материалы и методы: Исследование проводилось на смешанной культуре нейронов гиппокампа от самцов мышей в возрасте 9 дней линии CD-1, полученной через 24 часа после моделирования гипоксии-ишемии плода. Были сформированы следующие группы: Интактная культура; Культура ГИП; ГИП +rhHSP70 10-6М; ГИП +rhHSP70 10-8М; ГИП +rhHSP70 10-9М ; ГИП +rhHSP70 10-12М с добавлением вещества в разведениях от исходной дозы 0,1 мкг/гр. Было проведено измерение модуля Юнга в режиме силовой спектроскопии, составлены карты локальной упругости различных участков поверхности.
Результаты и обсуждения: Модель гипоксии-ишемии плода вызывает увеличение жесткости клеточной поверхности нейронов гиппокампа на 18% (р<0,001) в сравнении с группой контроля (p<0,001). При добавлении к культуре ГИП rhHSP70 10-6М, rhHSP70 10-8М привело к повышению жесткости мембраны на 20%( р<0,001), 3% (p<0,0034) и снижению жесткости мембраны в разведении rhHSP70 10-9М, rhHSP70 10-12М на 35%(p<0,001) и на 22%(р<0,001) в сравнении с интактной группой соответственно. В сравнении с группой культуры нейронов после моделирования неонатальной гипоксии ишемии жесткость мембраны в с добавлением rhHSP70 10-8М, rhHSP70 10-9М ,rhHSP70 10-12М снизилась на 17%(p<0,0004), 65%( p<0,001), 49%( р<0,001).
Заключение: Таким образом, добавление rhHSP 70 вызывает снижение жесткости мембраны смешанной культуры нейронов гиппокампа у мышей как в сравнении с интактной полученной после проведения неонатальной гипоксии ишемии культуре. Метод АСМ позволяет оценивать, как различные молекулы, такие как белки теплового шока (например, rhHSP70), влияют на механические свойства мембраны, что может быть критически важно для разработки новых лекарств.
Графическая аннотация
Ключевые слова:
HSP 70, гипоксия-ишемия плода, модуль Юнга, мембрана нейронов гиппокампа, АСМБиблиографические ссылки
Belenichev IF, Aliyeva OG, Popazova OO, Bukhtiyarova NV (2023) Involvement of heat shock proteins HSP70 in the mechanisms of endogenous neuroprotection: the prospect of using HSP70 modulators. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 17(1): 113–168. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2023.1131683 [PubMed] [PMC]
Bryniarska-Kubiak N, Kubiak A, Trojan E, Wesołowska J, Lekka M, Basta-Kaim A (2023) Oxygen-glucose deprivation in organotypic hippocampal cultures leads to cytoskeleton rearrangement and immune activation: link to the potential pathomechanism of ischemic stroke. Cells 12: 1465. https://doi:10.3390/cells12111465 [PubMed] [PMC]
Cartagena-Rivera AX, Wang WH, Geahlen RL, Raman A (2015) Fast, multi-frequency, and quantitative nanomechanical mapping of live cells using the atomic force microscope. Scientific Reports 5: 11692. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11692[PubMed] [PMC]
Cheirdaris D (2022) Visualizing Neurodegeneration Using Atomic Force Microscopy. Handbook of Computational Neurodegeneration ( 4): 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75479-6_4-2
Chighizola M, Dini T, Lenardi C, Milani P, Podestà A, Schulte C (2019) Mechanotransduction in neuronal cell development and functioning. Biophysical reviews 11: 701–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-019-00587-2 [PubMed][PMC]
Dabral S, Muecke C, Valasarajan C, Schmoranzer M, Wietelmann A, Semenza GL, Meister M, Muley T, Seeger-Nukpezah T, Samakovlis C, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Savai R, Pullamsetti SS (2019) A RASSF1A-HIF1α loop drives Warburg effect in cancer and pulmonary hypertension. Nature Communications 10(1): 2130 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10044-z [PubMed] [PMC]
DeGiosio RA, Grubisha MJ, MacDonald ML, McKinney BC, Camacho CJ, Sweet RA (2022) More than a marker: Potential pathogenic functions of MAP2. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 15: 974890. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2022.974890 [PubMed] [PMC]
Demyanenko S, Nikul V, Rodkin S, DavletsHIn A, Evgen'ev MB, Garbuz DG (2021) Exogenous recombinant Hsp70 mediates neuroprotection after photothrombotic stroke. Cell Stress and Chaperones 26(1): 103–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01159-0 [PubMed] [PMC]
Dukay B, Csoboz B, Tóth ME (2019) Heat-shock proteins in neuroinflammation. Frontiers in Pharmacology 10: 920–931 https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00920 [PubMed] [PMC]
Frederix PL, Bosshart PD, Engel A (2009) Atomic force microscopy of biological membranes. Biophysical Journal 96(2): 329–338. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2008.09.046 [PubMed] [PMC]
Galvanetto N (2018) Single-cell unroofing: probing topology and nanomechanics of native membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) – Biomembranes 1860: 2532–2538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.06.011 [PubMed]
Guimarães CF, Gasperini L, Marques AP, Reis RL (2020) The stiffness of living tissues and its implications for tissue engineering. Nature Reviews Materials 5: 351–370. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-019-0120-8
Guo CY, Xiong TQ, Tan BH, Gui Y, Ye N, Li SL, Li YC (2019) The temporal and spatial changes of actin cytoskeleton in the hippocampal CA1 neurons following transient global ischemia. Brain research 17(20): 1462–1497. https://doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2019.06.016 [PubMed]
Guo CY, Xiong TQ, Tan BH, Gui Y, Ye N, Li SL, Li YC (2019) The temporal and spatial changes of actin cytoskeleton in the hippocampal CA1 neurons following transient global ischemia. Brain Research 1720: 146297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2019.06.016 [PubMed]
Handorf AM, Zhou Y, Halanski MA, Li W-J (2015) Tissue stiffness dictates development, homeostasis, and disease progression. Organogenesis 11(1): 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476278.2015.1040571 [PubMed] [PMC]
Kiio TM, Park S (2020) Nano-scientific application of atomic force microscopy in pathology: from molecules to tissues. International journal of medical sciences17: 844–858. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.41805 [PubMed] [PMC]
Kiral FR, Kohrs FE, Jin EJ, Hiesinger PR (2018) Rab GTPases and membrane trafficking in neurodegeneration. Current Biology 28(8): 471–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.010 [PubMed] [PMC]
Leu JI, Barnoud T, Zhang G, Tian T, Wei Z, Herlyn M (2017) Inhibition of stress-inducible HSP70 impairs mitochondrial proteostasis and function. Oncotarget 8: 45656–45669. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17156 [PubMed] [PMC]
Leu JI, Barnoud T, Zhang G, Tian T, Wei Z, Herlyn M, Murphy ME, George DL (2017) Inhibition of stress-inducible HSP70 impairs mitochondrial proteostasis and function. Oncotarget 8(28): 45656–45669. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17321 [PubMed] [PMC]
Levenson RW, Sturm VE, Haase CM (2014) Emotional and behavioral symptoms in neurodegenerative disease: a model for studying the neural bases of psychopathology. Annual review of clinical psychology 10: 581–606. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032813-153653 [PubMed] [PMC]
Mishra AK, Tripathi MK, Kumar D, Gupta SP (2024) Neurons specialize in presynaptic autophagy: A perspective to ameliorate neurodegeneration. Molecular Neurobiology https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-024-04399-8 [PubMed]
Nakano F, Liu L, Kawakita F, Kanamaru H, Nakatsuka Y, Nishikawa H, Okada T, Shiba M, Suzuki H (2019) Morphological characteristics of neuronal death after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice using double immunoenzymatic technique. The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 67(12): 919–930. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155419878181 [PubMed] [PMC]
Ohashi K, Fujiwara S, Mizuno K (2017) Roles of the cytoskeleton, cell adhesion and Rho signaling in mechanosensing and mechanotransduction. The Journal of Biochemistry 161(3): 245–254 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-019-0169-1[PubMed]
Papa L, Robicsek SA, Brophy GM, Wang KK, Hannay HJ, Heaton S, Schmalfuss I, Gabrielli A, Hayes RL, Robertson CS (2018) Temporal profile of microtubule-associated protein 2: A novel indicator of diffuse brain injury severity and early mortality after brain trauma. Journal of Neurotrauma 35(1):32–40. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2017.4994 [PubMed][PMC]
Pluta R, Ouyang L, Januszewski S, Li Y, Czuczwar SJ (2021) Participation of amyloid and tau protein in post-ischemic neurodegeneration of the hippocampus of a nature identical to Alzheimer’s disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22: 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052460 [PubMed] [PMC]
Pluta R, Ułamek-Kozioł M, Januszewski S, Czuczwar SJ (2019) Amyloid pathology in the brain after ischemia. Folia Neuropathologica 57(3): 220–226. https://doi.org/10.5114/fn.2019.88450 [PubMed] [PubMed] [PMC]
Qin C, Yang S, Chu YH, Zhang H, Pang XW, Chen L, Zhou LQ, Chen M, Tian DS, Wang W (2022) Signaling pathways involved in ischemic stroke: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 7: 215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01064-1 [PubMed] [PMC]
Radenovic L, Nenadic M, Ułamek-Kozioł M, Januszewski S, Czuczwar SJ, Andjus PR, Pluta R (2020) Heterogeneity in brain distribution of activated microglia and astrocytes in a rat ischemic model of Alzheimer’s disease after 2 years of survival. Aging 12(12): 12251–12267. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103411 [PubMed] [PMC]
Seano G, Nia HT, Emblem KE, Datta M, Ren J, Krishnan S, Kloepper J, Pinho MC, Ho WW, Ghosh M (2019) Solid stress in brain tumours causes neuronal loss and neurological dysfunction and can be reversed by lithium. Nature Biomedical Engineering 3: 230–245. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0334-7 [PubMed] [PMC]
Shao A, Zhou Y, Yao Y, Zhang W, Zhang J, Deng Y (2019) The role and therapeutic potential of heat shock proteins in haemorrhagic stroke. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 23(9): 5846–5858. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14479[PubMed] [PMC]
Sheldon RA, Windsor C, Ferriero DM (2018) Strain-related differences in mouse neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 40(5-6): 490–496. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495880 [PubMed] [PMC]
Skorkina MYu, Fedorova MZ, Sladkova EA, Muravyov AV (2012) The use of nanomechanic sensor for studies of morphofunctional properties of lymphocytes from healthy donors and patients with chronic lymphoblastic leukemia. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 154(1): 163–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1899-x [PubMed]
Sun YY, Zhu HJ, Zhao RY, Zhou SY, Wang MQ, Yang Y, Guo ZN (2023) Remote ischemic conditioning attenuates oxidative stress and inflammation via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in MCAO mice. Redox Biology 66: 102852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2023.102852 [PubMed] [PMC]
Tirpe AA, Gulei D, Ciortea SM, Crivii C, Berindan-Neagoe I (2019) Hypoxia: overview on hypoxia-mediated mechanisms with a focus on the role of HIF genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20(24): 6140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246140 [PubMed] [PMC]
Tuo Q, Zhang S, Lei P (2021) Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Medicinal Research Reviews 42:259–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21773 [PubMed]
Vining KH, Mooney DJ (2017) Mechanical forces direct stem cell behavior in development and regeneration. Nature Reviews Materials 18(12): 728–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.81 [PubMed] [PMC]
Wilson KA, MacDermott-Opeskin HI, Riley E, Lin Y, O'Mara ML (2020) Understanding the link between lipid diversity and the biophysical properties of the neuronal plasma membrane. Biochemistry 59(33): 3010–301. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00524 [PubMed]
Wilson KA, MacDermott-Opeskin HI, Riley E, Lin Y, O'Mara ML (2020) Understanding the link between lipid diversity and the biophysical properties of the neuronal plasma membrane. Biochemistry. 59(33): 3010–3018 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00524 [PubMed]
Загрузки
Опубликован
Как цитировать
Выпуск
Раздел
Лицензия
Copyright (c) 2024 Pokrovsky VM, Deikin AV, T Zhang, Verlov NA, Konevega AL, Korokin MV

Это произведение доступно по лицензии Creative Commons «Attribution» («Атрибуция») 4.0 Всемирная.
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

