Analgesic activity of imidazo[1,2-a]indole derivative and its involvement of TRPV1 and κ-opioid receptors
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18413/rrpharmacology.11.641Abstract
Introduction: Various analgesics, primarily nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, are used to relieve pain. On the account that opioids can cause respiratory depression, psychological and physical dependence, as well as addiction, and NSAIDs can cause gastro- and enteropathy, nephrotoxicity, bronchospasm, bleeding, and cardiovascular dysfunction, the search for new molecules exerting an analgesic effect through other cellular targets is relevant. The aim of this study was to evaluate the analgesic effect of a new imidazo[1,2-a]indole derivative in various pain models and its effect on TRPV1 and κ-opioid receptors.
Materials and Methods. The median lethal dose (LD50) of the imidazo[1,2-a]indole derivative (lab code SV-1010) was determined in experiments on mice and rats. The analgesic effect of SV-1010 was studied by means of the hot plate test (in mice), tail-flick test (in rats), paw pressure test (in rats), abdominal constriction test (in mice), formalin test (in rats), and neuropathic pain test (in rats). In addition, the effect of SV-1010 on TRPV1 ion channels was examined (in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line with an induced expression of a rat TRPV1 channel), and the potential for κ-opioid receptor activation was tested (by means of molecular docking). SV-1010 and the reference drugs diclofenac, indomethacin, ketorolac, and pregabalin were administered intragastrically.
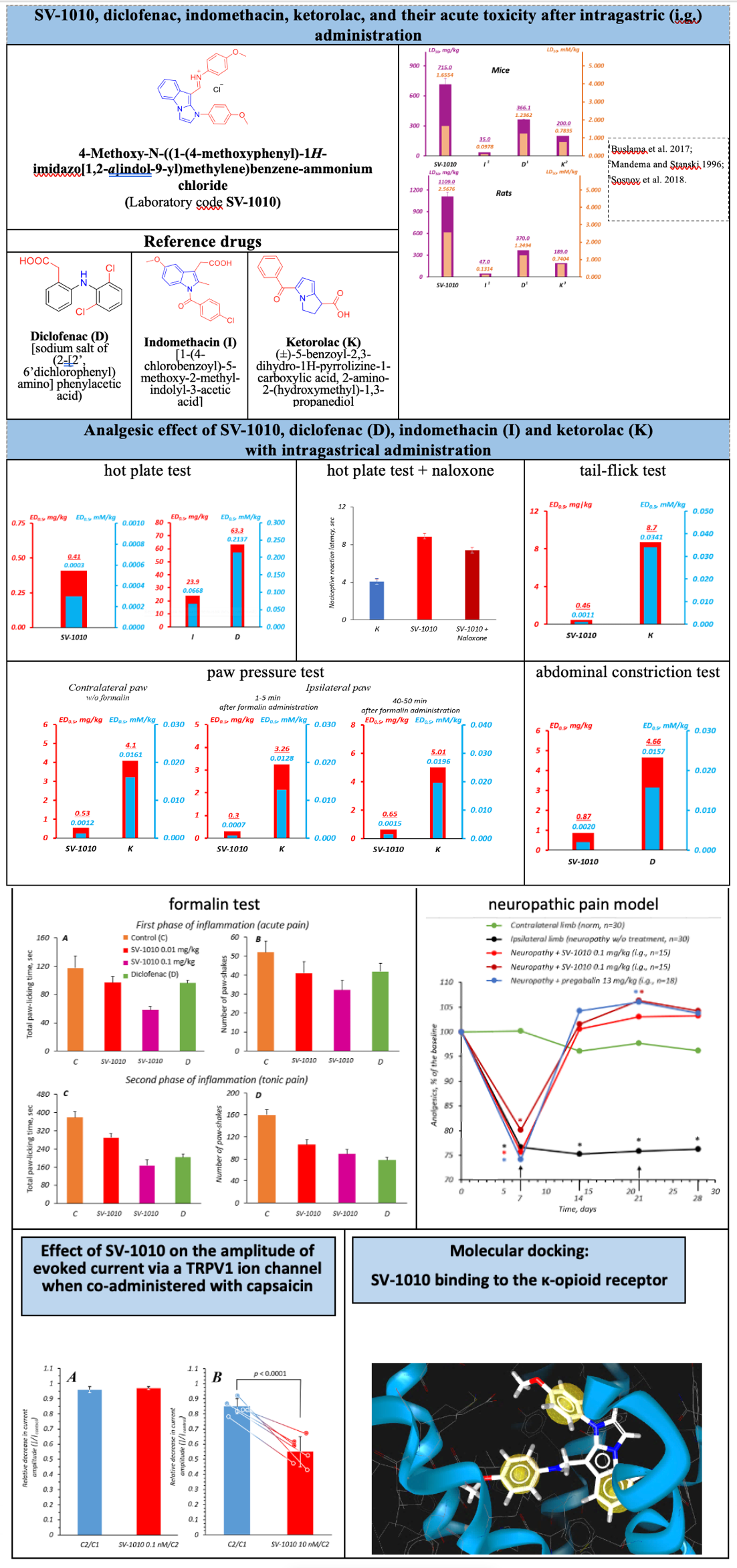
Results and Discussion: SV-1010 is less toxic than diclofenac, indomethacin, and ketorolac, exhibits a pronounced analgesic effect, but exceeds diclofenac, indomethacin, ketorolac, and pregabalin by the potency and therapeutic index. The treatment sites for SV-1010 to exert its analgesic effect are the supraspinal, supraspinal + peripheral, spinal, and peripheral levels of pain sensitivity. Of note is the high selectivity of SV-1010 to blocking TRPV1 ion channel and activating κ-opioid receptors.
Conclusion: Significantly lower acute toxicity (when compared to such of diclofenac, indomethacin, and ketorolac), high analgesic activity, and a wider therapeutic index (when compared to such of diclofenac, indomethacin, ketorolac, and pregabalin) make SV-1010 promising for further preclinical study.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords:
analgesic effect, imidazo[1,2-a]indole derivative, TRPV1 ion channels, κ-opioid receptorsReferences
Alawi K, Keeble J (2010) The paradoxical role of the transient receptor potential vaniloid 1 receptor in inflammation. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 125(2): 181–195. https://doi.org/1016/j.pharmthera.2009.10.005 [PubMed]
Aliforenko AE, Bykov VV, Bykova AV, Motov VS, Stankevich SA, Pavlovsky VI, Khazanov VA, Vengerovsky AI (2023) Analgesic activity of a bradykinin antagonist – a 1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one derivative. Bulletin of Siberian Medicine [Byulleten' Sibirskoj Mediciny] 22(2): 6–13. https://doi.org/10.20538/1682-0363-2023-2-6-13 [in Russian]
Arbukh DM, Abuzarova GR, Alekseeva GS (2017) Opioid analgesics in the treatment of pain syndromes (Part 1). Bulletin of Anesthesiology and Resuscitation [Vestnik Anesteziologii i Reanimatologii] 14(3): 58–67. https://doi.org/10.21292/2078-5658-2017-14-3-58-67 [in Russian]
Arzamastsev EV, Guskova TA, Berezovskaya IV (2000) Guidelines for the study of the general toxic action of pharmacological substances. In: Guide to the Experimental (Preclinical) Study of New Pharmacological Substances. Remedium Information and Publishing Agency, Moscow, pp. 18-24. [in Russian]
Buzlama AV, Nikolaevsky VA, Chernov YuN, Slivkin AI (2017) Preclinical Studies of Drugs: a tutorial. GEOTAR-Media, Moscow, 384 p. [in Russian]
Chaika AV, Cheretaev IV, Khusainov DR (2015) Methods of experimental preclinical trials of the analgesic effect of various factors in laboratory rats and mice. Proceedings of the Vernadsky Crimean Federal University. Biology. Chemistry [Uchenye zapiski Krymskogo Federal'nogo Universiteta Imeni V.I. Vernadskogo. Biologiya. Himiya] 1(1): 161–173. [in Russian]
Cherezov V, Stevens RC (2010) Structure of the human k-opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature 485(7398): 327–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10939 [PubMed] [PMC]
Erofeeva A-MV, Zhavoronok IP, Antipova OA, Schastnaya NI, Semenik IA, Ryabtseva SN, Molchanova AYu (2021) Evaluation of the antinociceptive effect of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in experimental peripheral neuropathic pain. Surgical News [Novosti Hirurgii] 29(5): 527–534. https://doi.org/10.18484/2305-0047.2021.5.527 [in Russian]
Galenko-Yaroshevsky PA, Pokrovsky MV, Nefedov DA, Pavlyuchenko II, Stepanyuk GI, Gulevskaya ON, Zelenskaya AV, Gudyrev OS, Uvarov AV, Chuyan EN, Ravaeva MYu, Manokhin AA (2021) Dimephosphone as a Dermatoprotective Agent in Reduced Skin Blood Circulation in Patients with Normoglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus. Prosveshchenie-Yug, Krasnodar, 210 pp. [in Russian]
Gregory NS, Harris AL, Robinson CR, Dougherty PM, Fuchs PN, Sluka KA (2013) An overview of animal models of pain: disease models and outcome measures. Journal of Pain 14(11): 1255–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2013.06.008 [PubMed] [PMC]
Ivanova EA, Matyushkin AI, Voronina TA (2023) Analysis of the involvement of NMDA receptors in analgesia and hypothermia caused by activation of TRPV1 ion channels. Acta Naturae 15(1): 42–50. https://doi.org/10.32607/actanaturae.11829 [PubMed] [PMC]
Kamchatnov PR, Chugunov AV, Chipova DT, Kazakov AYu (2023) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of heart failure. Russian Medical Journal 2: 88–95. [in Russian]
Karateev AE, Nasonov EL, Ivashkin VT, Martynov AI, Yakhno NN, Arutyunov GP, Alekseeva LI, Abuzarova GR, Evseev MA, Kukushkin ML, Kopenkin SS, Lila AM, Lapina TL, Novikova DS, Popkova TV, Rebrov AP, Skorobogatykh KV, Chichasova NV (2018) Efficient use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clinical guidelines. Scientific and Practical Rheumatology [Nauchno-Prakticheskaya Revmatologiya] 56: 1–29. https://doi.org/10.14412/rjtao20180 [in Russian]
Khoroshun MS, Lazareva AA (2022) Prescribing nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Benefits and risks. University Therapeutic Bulletin [Universitetskij Terapevticheskij Vestnik] 4(1): 4–10. https://doi.org/10.56871/3854.2022.69.43.001 [in Russian]
Kirkpatrick DR McEntire DM, Smith TA, Dueck NP, Kerfeld MJ, Hambsch ZJ, Nelson TJ, Reisbig MD, Agrawal DK (2016) Transmission pathways and mediators as the basis for clinical pharmacology of pain. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 9(10): 1363–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2016.1204231 [PubMed] [PMC]
Koob GF (2020) Neurobiology of opioid addiction: Opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biological Psychiatry 87(1): 44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023 [PubMed]
Lanas A, Chan FKL (2017) Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 390(10094): 613-624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023 [PubMed]
Litchfield Jr. JT, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 96(2): 99–113. [PubMed]
Listos J, Łupina M, Talarek S, Mazur A, Orzelska-Górka J, Kotlińska J (2019) The mechanisms involved in morphine addiction: An overview. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20(17): 4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174302 [PubMed] [PMC]
Mandema JW, Stanski DR (1996) Population pharmacodynamic model for ketorolac analgesia. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 60(6): 619–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-9236(96)90210-6 [PubMed]
Mashkovsky MD (2021) Medicines: in 2 volumes. Vol. 1. 16th, revised, corrected, and expanded. Novaya Volna Publishing House, Moscow, 1216 pp. IBSN 978-5-7864-0218-7 [in Russian]
Minhas D, Nidhaan A, Husni ME (2023) Recommendations for the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cardiovascular disease risk: Decades later, any new lessons learned? Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America 49(1): 179–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2022.08.006 [PubMed]
Mironov AN (2012) Guidelines for Conducting Preclinical Studies of Drugs. Grif i K, Moscow, 944 pp. [in Russian]
Papalia GF, Russo F, Vadalà G, Pascarella G, De Salvatore S, Ambrosio L, Di Martino S, Sammartini D, Sammartini E, Carassiti M, Papalia R, Denaro V (2022) Non-invasive treatments for failed back surgery syndrome: A systematic review. Global Spine Journal 13(4): 1153–1162. https://doi.org/10.1177/21925682221141385 [PubMed] [PMC]
Pereira V, Goudet C (2019) Emerging trends in pain modulation by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 11: 464. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00464 [PubMed] [PMC]
Prozorovsky VB (1962) Using the least squares method for probit analysis of mortality curves. Pharmacology and Toxicology [Farmakologiya i Toksikologiya] 1: 115–119. [in Russian]
Raevsky KS (1976) Pharmacology of Neuroleptics. Medicine, Moscow, 271 pp. [in Russian]
Rizi F, Ruzza C, Bianco S, Trapella C, Calo G (2017) Antinociceptive action of NOP and opioid receptor agonists in the mouse orofacial formalin test. Peptides 94: 71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2017.07.002 [PubMed]
Sosnov AV, Semchenko FM, Tokhmakhchi VN, Sosnova AA, Vlasov MI, Radilov AS, Krivorotov DV (2018) Criteria for selecting compounds for the development of potent analgesics and other centrally acting drugs. Drug Development and Registration [Razrabotka i Registraciâ Lekarstvennyh Sredstv] 3: 114–128. [in Russian]
Szallasi A, Cortright DN, Blum CA, Eid SR (2007) The vanilloid receptor TRPV1: 10 years from channel cloning to antagonist proof-of-concept. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 6(5): 357–372. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2280 [PubMed]
Titova NV, Bezdolny YuN (2025) Failed back surgery syndrome as a multidisciplinary problem. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapy [Klinicheskaya Farmakologiya i Terapiya] 34(2): 51–58. https://doi.org/10.32756/0869-5490-2025-2-51-58 [in Russian]
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. Journal of Computational Chemistry 31(2): 455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334 [PubMed] [PMC]
Vasiliev PM, Spasov AA, Kochetkov AN, Vorfolomeeva VV, Yanalieva LR (2016) Consensus approach to the in silico search for antidiabetic compounds. In: Spasov AA, Petrova VI (Eds). Target-oriented Search for Antidiabetic Agents. Publishing House of Volgograd State Medical University, Volgograd, 2016, pp. 126-181. [in Russian]
Velts NYu, Zhuravleva EO, Bukatina TM, Kutekhova GV (2018) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: safety issues. Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy [Bezopasnostʹ i Risk Farmakoterapii] 6(1): 11–18. https://doi.org/10.30895/2312-7821-2018-6-1-11-18 [in Russian]
Voronina TA, Guzevatykh LS (2012) Guidelines for studying the analgesic activity of drugs. In: Mironov AN (Ed) Guidelines for Conducting Preclinical Studies of Drugs. Grif i K, Moscow, pp. 197-219. [in Russian]
Wheeler-Aceto H, Cowan A (1991) Standardization of the rat paw formalin test for the evaluation of analgesics. Psychopharmacology 104(1): 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244551 [PubMed]
Wu H, Wacker D, Mileni M, Katritch V, Won HG, Vardy E, Liu W, Thompson AA, Huang X-P, Carroll FI, Mascarella SW, Westkaemper RB, Mosier PD, Roth BL, Cherezov V, Stevens RC (2010) Structure of the human k-opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature 485(7398): 327–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10939 [PubMed] [PMC]
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Galenko-Yaroshevsky PA, Zelenskaya AV, Suzdalev KF, Chuyan EN, Ravaeva MYu, Murashko RA, Vassiliev PM, Glechyan TR, Sergeeva AV, Leychenko EV, Chubinsky-Nadezhdin VI, Gulevskaya ON, Korolkova YuV, Shamatova MM, Vasileva VYu, Ishkhanyan NN, Kozlov SA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 Русский
Русский
 English
English

